The Endocrine System Linda Lu and Veleda Tam Biology Diagrams The endocrine pancreas plays a dominant role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis through the coordinated but opposing actions of glucagon-producing α cells and insulin-producing β cells (1, 2).Disturbances in this regulatory network result in debilitating diseases such as type 2 diabetes (T2D) mellitus, which affects more than 425 million people worldwide and is a leading cause of death As mentioned above, pancreatic glucagon's metabolic functions are in many respects opposite to those of insulin. Glucagon's most prominent physiological role is to stimulate glucose production via hepatic glycogenenolysis or gluconeogensis, thereby helping maintain euglycemia during states of rapid glucose utilization or fasts, respectively.
+Glucagon.jpg)
The pancreatic islets of Langerhans are central to fine-tuning metabolism to ensure metabolic homeostasis during the transition between fasting and feeding. Insulin and glucagon, the principal

How insulin and glucagon regulate blood sugar Biology Diagrams
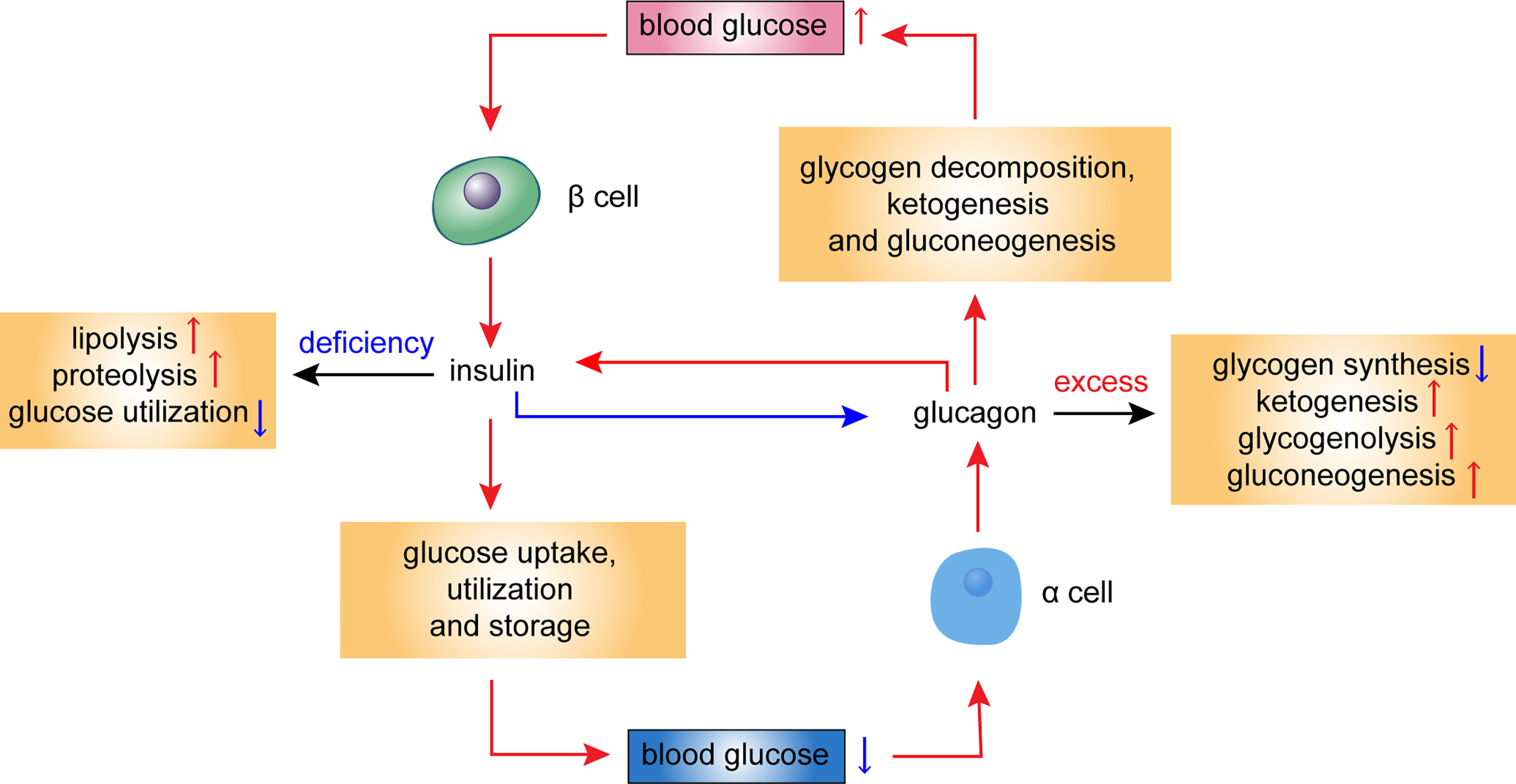
Metabolic homeostasis in mammals is tightly regulated by the complementary actions of insulin and glucagon. The secretion of these hormones from pancreatic β-cells and α-cells, respectively, is
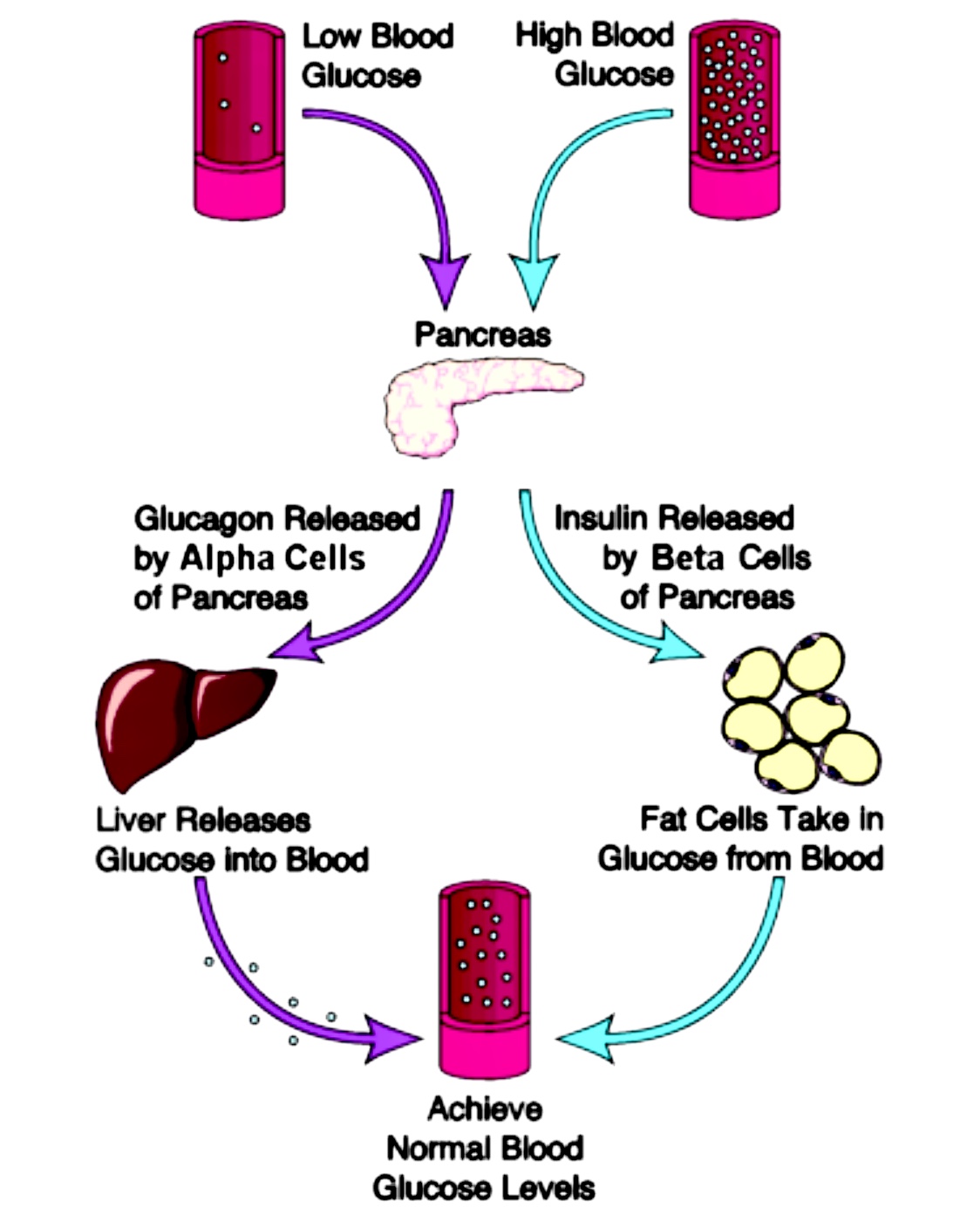
Abstract. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone mainly secreted by β cells in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas. The hormone potentially coordinates with glucagon to modulate blood glucose levels; insulin acts via an anabolic pathway, while glucagon performs catabolic functions. Glucose homeostasis is mainly under the control of the pancreatic islet hormones insulin and glucagon, which, respectively, stimulate glucose uptake and utilization by liver, fat, and muscle and glucose production by the liver. The balance between the secretions of these hormones is under the control of blood glucose concentrations. Glucagon increases blood glucose levels, whereas insulin decreases them. 5 Somatostatin inhibits both, glucagon and insulin release, 6 whereas PP regulates the exocrine and endocrine secretion activity of the pancreas. 3, 7 Altogether, these hormones regulate glucose homeostasis in vertebrates, as described in more detail below. Although the

Pancreatic signals controlling food intake; insulin, glucagon and ... Biology Diagrams
Through its various hormones, particularly glucagon and insulin, the pancreas maintains blood glucose levels within a very narrow range of 4-6 m M. This preservation is accomplished by the
Together, insulin and glucagon help maintain homeostasis, where conditions inside the body hold steady. When a person's blood sugar is too high, their pancreas secretes more insulin. When their
