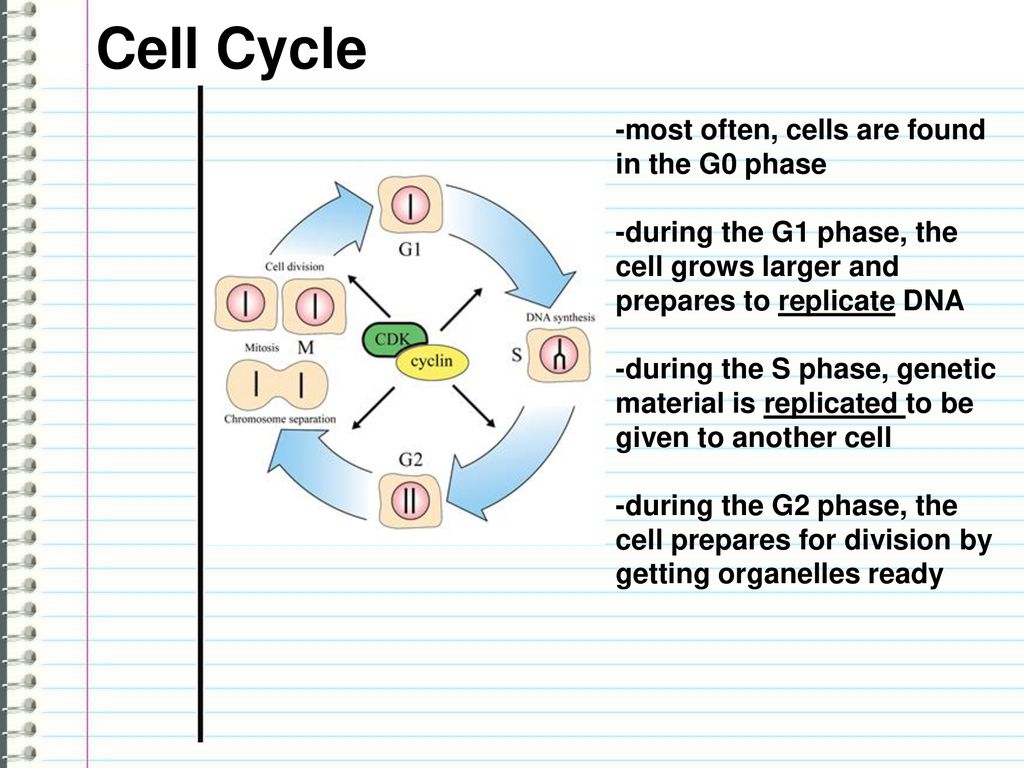
space for C II O I 12 CO and FIR Biology Diagrams For most quiescent cells, this arrest takes place in G0, a resting phase outside of the cell cycle that occurs prior to S phase, Heldt FS, Butera F, Stoy H, Mansfeld J, Novak B, and Bakal C (2017). DNA damage during S-phase mediates the proliferation-quiescence decision in the subsequent G1 via p21 expression. Nat Commun 8, 14728.

Three G 0 states exist and can be categorized as either reversible or irreversible (senescent and differentiated).Each of these three states can be entered from the G 1 phase before the cell commits to the next round of the cell cycle. Quiescence refers to a reversible G 0 state where subpopulations of cells reside in a 'quiescent' state before entering the cell cycle after activation in

What is Quiescence? Biology Diagrams
Historically, the G0 phase of the cell cycle was referred to as an inactive, non-cycling state. It was first recognized and described as a state in which cells have irreversibly exited the cell cycle, Quiescence is also a state of growth cessation that occurs in multicellular organisms.
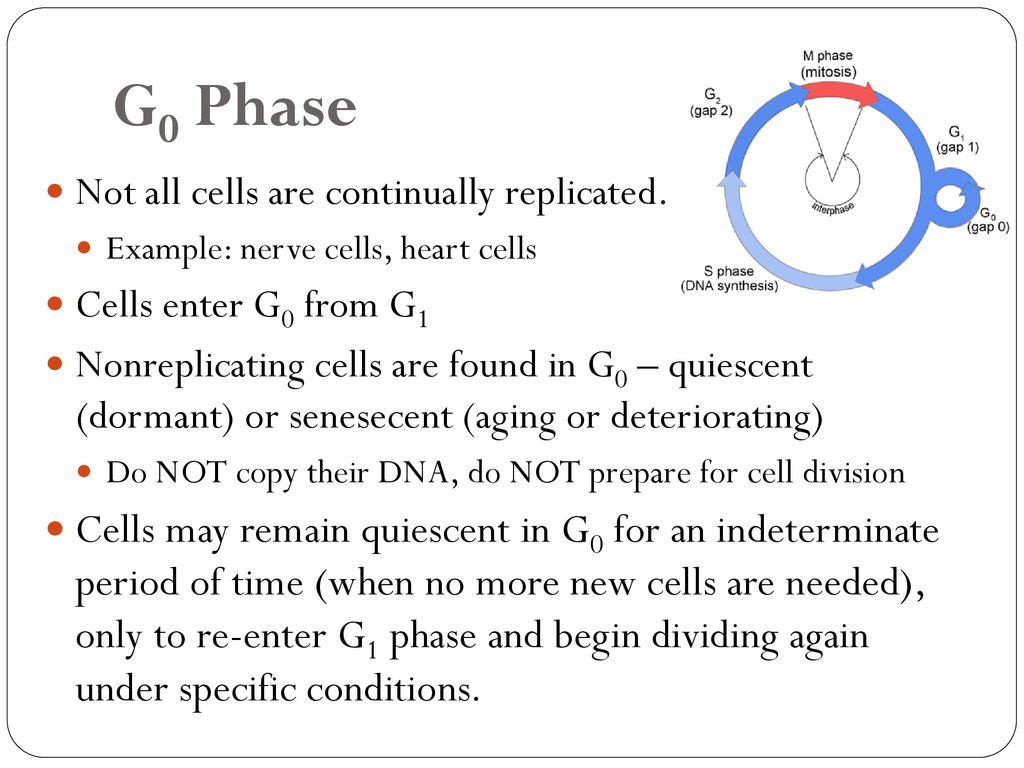
The capacity of cells to re-enter the G1 phase of the cell cycle from the G0 phase is a distinguishing feature of quiescence. Unlike quiescence, in which cell cycle arrest is reversible, terminal differentiation involves regeneration via cell differentiation from stem cells while remaining in the G0 phase (Hernandez-Segura, Nehme, & Demaria
Molecular regulation of stem cell quiescence Biology Diagrams
The process of phase separation, which is involved in the formation of membrane-less organelles (Boeynaems et al., 2018), is also emerging as a regulator of adult stem cell quiescence. In quiescent MuSCs, the microRNA miR-31 and its target Myf5 are sequestered in membrane-less messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) granules. Oocytes in female mammals become arrested at prophase I of meiosis, in contrast to other cell types that enter quiescence in G0 (described below). For most quiescent cells, this arrest takes place in G0, a resting phase outside of the cell cycle that occurs prior to S phase, but is distinct from the G1 phase observed in cycling cells